Evidence based
Prevalence
Research done by ASHA (American Speech-, Language and Hearing Association) shows that dysphagia is a very common condition having important medical as well as social impacts that drastically decrease a patient’s quality of life.

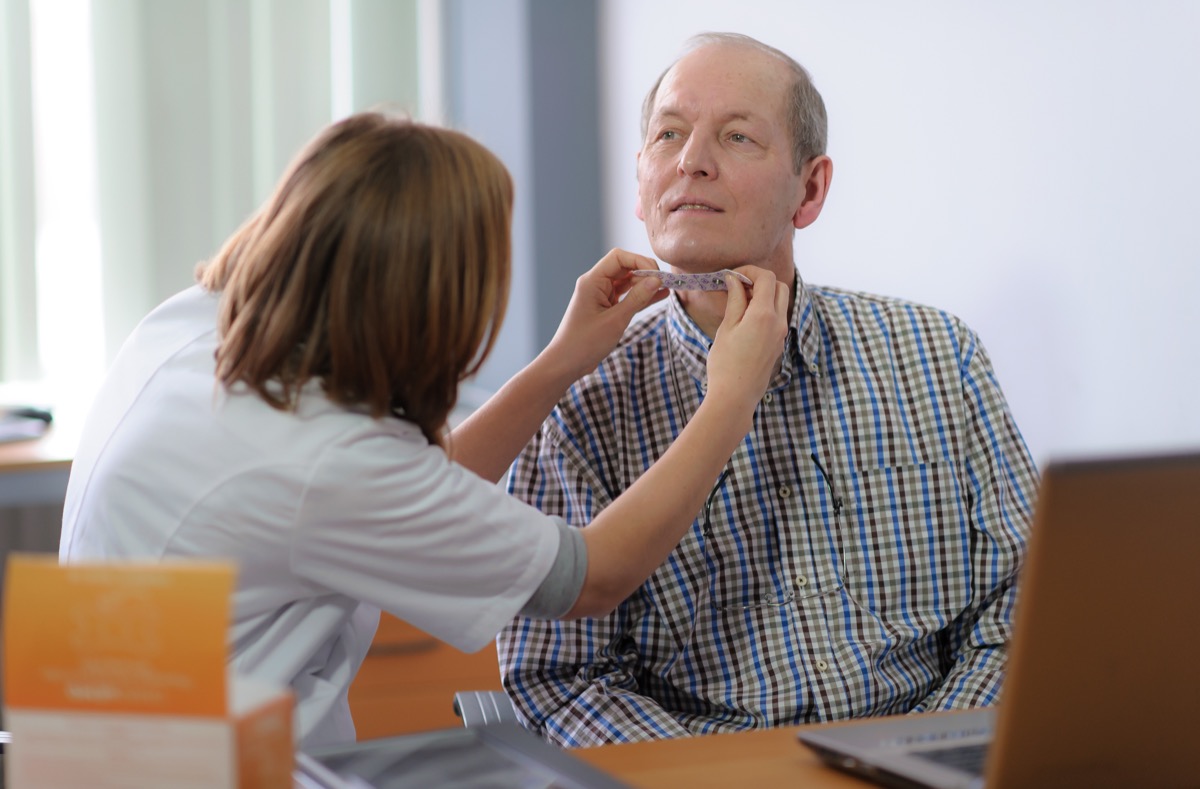
Rephagia: adjunctive surface electro myography (sEMG)
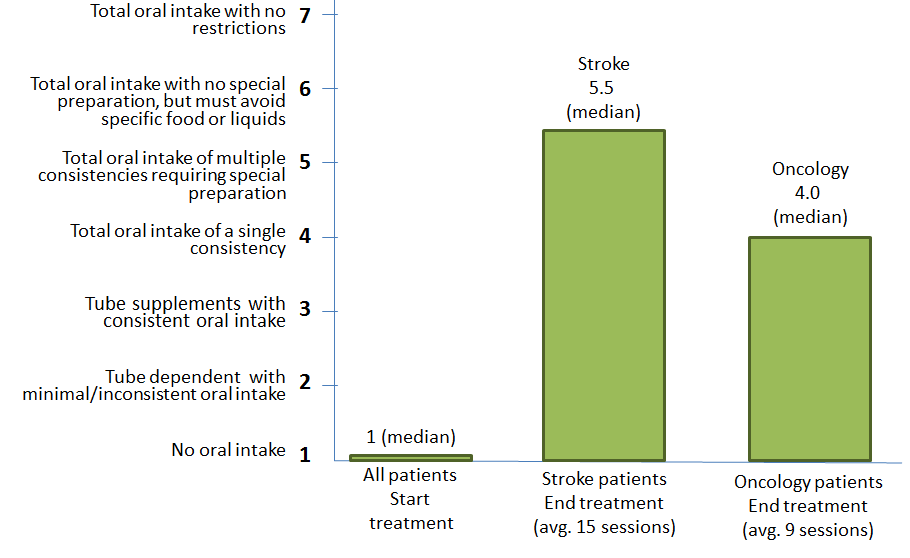
There is an accumulating body of research in which sEMG is used for rehabilitation of swallowing disorders. Biofeedback from sEMG has been widely described to be effective improving both oral and pharyngeal aspects of the swallow (Crary & Groher, 2000). The graph below illustrates the beneficial impact of sEMG on an oral intake for post-stroke survivors and oncology patients.
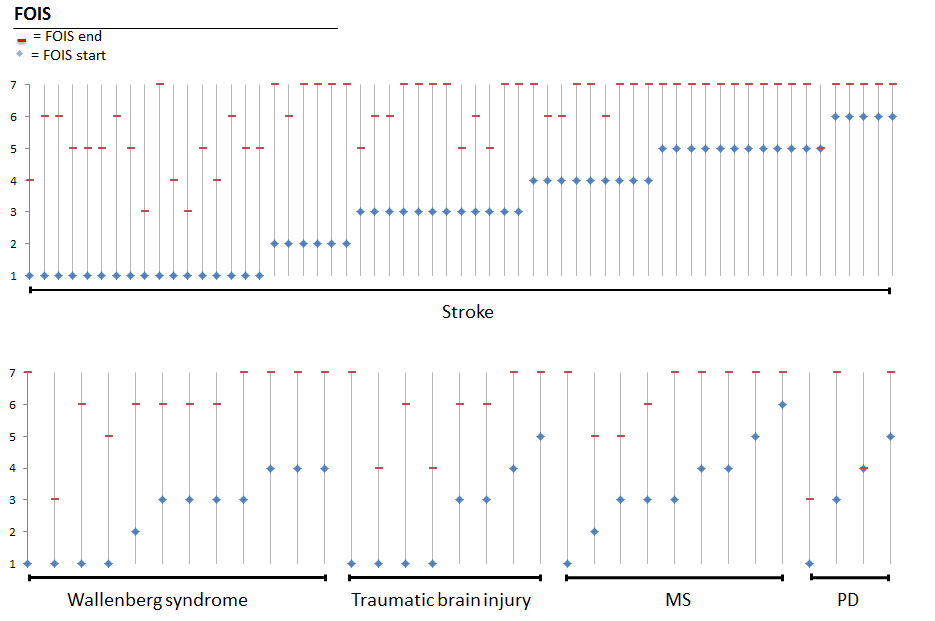
Impact
The graph below summarizes the impact of the proposed protocol in one of our test locations. A total of 94 patients underwent treatment. On average, the patients improved 3 steps on the 7-point FOIS score. Brain trauma and Wallenberg patients improved the most (3.5 and 3.6 steps, respectively) and patients with Parkinson’s disease showed more moderate improvement (2 steps).
Literature
- Asha Communication Facts (2008). Special Populations: Dysphagia. American Speech- Language-Hearing Association.
- Asha Prevalence of speech, voice and language disorders in the United States (1994). American Speech-Language-Hearing Association.
- Carnaby-Mann G.D., Crary M.A. (2010). McNeill Dysphagia Therapy Program: a case-control study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 91:743-9
- Crary, M.A., Carnaby-Mann, G.D, Groher, M.E., Helseth, E. (2004). MA: Functional Benefits of Dysphagia Therapy Using Adjunctive sEMG Biofeedback. Dysphagia, 19: 160-164 (2004), doi 10.1007/s00455004-0003-8
- Crary, M.A., Groher, M.E. (2000). Basic Concepts of Surface Electromyographic Biofeedback in the Treatment of Dysphagia: A Tutorial. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, Vol 9, 116125, ASHA 1058-0360/00/0902-0116
- Ekberg, O., Hamdy, S., Woisard, V., Wuttge-Hannig, A. & Ortega, P. (2002). Social and psychological burden of dysphagia:its impact on diagnosis and treatment. Dysphagia, 17: 139-146
- Kays, S., Robbins, J., (2006). Effects of Sensorimotor Exercise on Swallowing Outcomes relative to Age and Age-Related Disease. Seminars in Speech and Language, Vol 27, nr 4
- Kil-Byung Lim, M.D., et al. (2009). Neuromuscular electrical and thermal-tactile stimulation for dysphagia caused by stroke: a randomized control trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 41: 174–178
- Mann, G., Hankey, G.J., Cameron, D. (2000). Swallowing disorders following acute stroke: prevalence and diagnostic accuracy. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 10: 380-386, 2000.
- McCullough, G.H., Kamarunas, E., Mann, G.C., Schmidley, J.W., Robbins, J.A., Crary, M.A. (2012). Effects of Mendelsohn Maneuver on Measures of Swallowing Duration Post Stroke. Top Stroke Rehabilitation, Volume 19, Issue 3, pp. 234-243
- McCullough, G.H., Kim, Y. (2013). Effects of Mendelsohn Maneuver on Extent of Hyoid Movement and use Opening PostStroke. Dysphagia, 28:511-519.
- Medicare (2001-2002). data from Medicare Standard Analytic File
- Nguyen, N.P., Frank, C., Moltz, C.C., Vos, P., Smith, H.J., Bhamidipati, P.V., Karlsson, U., Nguyen, P.D., Alfieri, A., Nguyen, L.M., Lemanski, C., Chan, W., Rose, S., Sallah, S. (2006). Aspiration rate following chemoradiation for head and neck cancer: an underreported occurrence. Radiotherapy and Oncology 80: 302-306
- Nguyen, N.P., Moltz, C.C., Frank, C., Vos, P., Smith, H.J., Karlsson, U., Nguyen, L.M., Rose, S., Dutta, S., Nguyen, N., Sallah. S. (2008). Long-term aspiration following treatment for head and neck cancer. Oncology, 74: 25-30
- Robbins, J.A., Kays, S.A., Gangnon, R.E., Hind, J.A., Hewitt, A.L., Gentry, L.R., Taylor, A.J. (2007). The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,88:150–158.
- Steele, C.M., Bennett, J.W., Chapman-Jay, S., Polacco, R.C., Molfenter, S.M., Oshalla, M. (2012). Electromyography as a Biofeedback Tool for Rehabilitating Swallowing Muscle Function. Applications of EMG in Clinical and Sports Medicine, ISBN 978953-307-798-7
- Stepp, C.E. (2012). Surface Electromyography for Speech and Swallowing Systems: Measurement, Analysis, and Interpretation. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, vol. 55, 1232-1246 ASHA
- Stepp, C.E., Britton, D., Chang, C., Merati, A.L., Matsuoka, Y. (2011). Feasibility of game-based electro- myographic biofeedback for dysphagia rehabilitation. Proceedings of the 5th International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, 978-1-4244-4141-9/11
 Nederlands
Nederlands  English
English  Français
Français  Deutsch
Deutsch